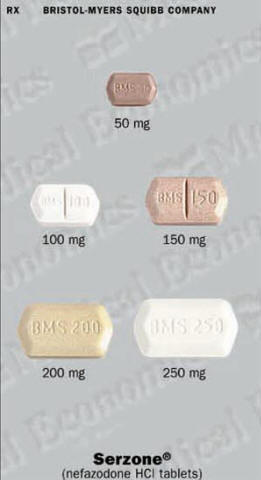
Serzone (Nefazodone) Patient Information
Find out why Nefazodone (Serzone) is prescribed, side effects of Serzone, Serzone warnings, effects of Serzone during pregnancy, more - in plain English.
Generic name: Nefazodone hydrochloride
Brand name: Serzone
Pronounced: sur-ZONE
Full Serzone Prescribing Information
Why is Serzone prescribed?
Serzone is prescribed for the treatment of depression severe enough to interfere with daily functioning. Possible symptoms include changes in appetite, weight, sleep habits, and mind/body coordination, increased fatigue, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, difficulty concentrating, slowed thinking, and suicidal thoughts.
Most important fact about Serzone
Sale of Serzone was discontinued in 2003 in some countries (U.S., Canada and others), due to the small possibility of hepatic (liver) injury, which could lead to the need for a liver transplant, or even death. Several generic formulations of nefazodone are still available.
It may be several weeks before you feel the full antidepressant effect of Serzone. Once you do begin to feel better, it is important to keep taking the drug.
How should you take Serzone?
Take Serzone exactly as prescribed by your doctor even if you no longer feel depressed. Your doctor should check your progress periodically.
--If you miss a dose...
Take it as soon as you remember. If it is within 4 hours of your next dose, skip the one you missed and go back to your regular schedule. Do not take 2 doses at once.
--Storage instructions...
Store at room temperature in a tightly closed container.
What side effects may occur with Serzone?
Side effects cannot be anticipated. If any develop or change in intensity, tell your doctor as soon as possible. Only your doctor can determine if it is safe for you to continue taking Serzone.
-
More common side effects of Serzone may include: Blurred or abnormal vision, confusion, constipation, dizziness, dry mouth, light-headedness, nausea, sleepiness, weakness
-
Less common side effects may include: Abnormal dreams, cough, decreased concentration, diarrhea, dizziness on getting up, flu-like symptoms, headache, increased appetite, water retention
-
Rare side effects may include: Abnormal bleeding, anxiety, blisters in mouth and eyes, breast pain, breast-milk discharge, breast enlargement in males, chills, coma, decreased sex drive, difficulty urinating, exaggerated reflexes, fever, frequent urination, lack of coordination, liver disease, prolonged erections, rigidity, ringing in ears, seizures, severe allergic reactions, spasms, stiff neck, sweating, taste change, thirst, tremors, urinary tract infection, vaginal inflammation
Why should Serzone not be prescribed?
If you are sensitive to or have ever had an allergic reaction to Serzone or similar drugs, such as Desyrel, you should not take this medication. You should also avoid it permanently if previous treatment had to be stopped due to signs of liver injury.
Serious, sometimes fatal reactions have occurred when Serzone is used in combination with drugs known as MAO inhibitors, including the antidepressants Nardil and Parnate. Never take Serzone with one of these drugs; and do not begin therapy with Serzone within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with one of them. Also, allow at least 7 days between the last dose of Serzone and the first dose of an MAO inhibitor.
Serzone should also be avoided if you are taking Halcion or Tegretol, and should never be combined with Orap, as heart problems could result.
Special warnings about Serzone
Your doctor will prescribe Serzone with caution if you have a history of seizures or mania (extreme agitation or excitability) or heart or liver disease. Serzone should also be used with caution if you have had a heart attack, stroke, or angina; take drugs for high blood pressure; or suffer from dehydration. Under these circumstances, Serzone could cause an unwanted drop in blood pressure. Be sure to discuss all of your medical problems with your doctor before taking this drug.
Serzone has also been known to produce very rare cases of potentially fatal liver failure. Ordinarily, the drug is not prescribed for people with liver disease, and your doctor may periodically test your liver function. If you develop warning signs of liver problems--such as loss of appetite, stomach upset, a generally ill feeling, or yellowing of the skin and eyes--alert your doctor immediately. Treatment with Serzone will probably have to be stopped.
Serzone may cause you to become drowsy or less alert and may affect your judgment. Do not drive or operate dangerous machinery or participate in any hazardous activity that requires full mental alertness until you know how the drug affects you.
Before having surgery, dental treatment, or any diagnostic procedure requiring anesthesia, tell the doctor or dentist you are taking Serzone. If you develop an allergic reaction such as a skin rash or hives while taking Serzone, notify your doctor. If you are male and experience a prolonged or inappropriate erection while taking Serzone, discontinue this drug and call your doctor.
If you have ever been addicted to drugs, tell your doctor before you start Serzone.
Possible food and drug interactions when taking Serzone
If Serzone is taken with certain other drugs, the effects of either could be increased, decreased, or altered. It is especially important to check with your doctor before combining Serzone with the following:
Alcohol
Alprazolam (Xanax)
Antidepressants that boost serotonin levels, including Celexa, Luvox, Paxil, Prozac, and Zoloft
Buspirone (BuSpar)
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Cyclosporine (Neoral and Sandimmune)
Digoxin (Lanoxin)
Haloperidol (Haldol)
MAO inhibitors, including Nardil and Parnate
Pimozide (Orap)
The cholesterol-lowering drugs Lipitor, Mevacor, and Zocor
Triazolam (Halcion)
Special information if you are pregnant or breastfeeding
The effects of Serzone during pregnancy have not been adequately studied. If you are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant, tell your doctor immediately. Serzone should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Serzone may appear in breast milk. If this medication is essential to your health, your doctor may tell you to discontinue breastfeeding until your treatment with Serzone is finished.
Recommended dosage for Serzone
ADULTS
The usual starting dose for Serzone is 200 milligrams a day, divided into 2 doses. If needed, your doctor may increase your dose gradually to 300 to 600 milligrams a day.
CHILDREN
The safety and effectiveness of Serzone have not been established in children under 18 years of age.
OLDER ADULTS
The usual starting dose for older people and those in a weakened condition is 100 milligrams a day, taken in 2 doses. Your doctor will adjust the dose according to your response.
Overdosage of Serzone
Any medication taken in excess can have serious consequences. If you suspect an overdose, seek medical attention immediately.
Symptoms of Serzone overdose include:
- Nausea, sleepiness, vomiting
Full Serzone Prescribing Information
Detailed Info on Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments of Depression
APA Reference
Staff, H.
(2009, January 3). Serzone (Nefazodone) Patient Information, HealthyPlace. Retrieved
on 2024, June 20 from https://www.healthyplace.com/other-info/psychiatric-medications/patient-information-serzone-nefazodone